As we saw in the last article dehydration can negatively affect health and performance. Therefore it is essential to drink enough both before, during and after sport.
Although we know that we should drink often the question is, what should we drink especially on those long run days. The following article attempts to answer some of your questions regarding sports drinks and their contents.
When is it ok just to drink water?
In general, water is sufficient during exercise duration of 1 hour or less.
When should I take a sports drink/carbohydrate?
For endurance running of over 1 hour it is generally recommended that we consume 30g-60g of carbohydrate during each hour of sport, along with water.
Why do we need carbohydrates when we run for over 1 hour?
This carbohydrate source during exercise helps to fuel the brain and muscles and can be achieved either by adding the carbohydrate to your drink, taking gels or by eating snacks.
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are an ideal source of energy for the body and are an essential fuel source during exercise. Much research has shown that consuming carbohydrates during running will enhance performance and increase your endurance capability.
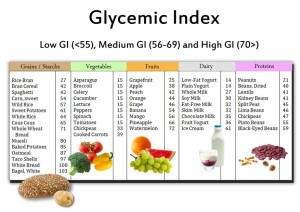
There are two types of carbohydrate: complex or low GI and simple or high GI. Complex carbohydrates provide a slower and more sustained release of energy than simple carbohydrates. All carbohydrates form glucose when digested. Glucose is transported around the body via blood and taken into cells to be converted into energy. The pancreas gland in your abdomen secretes the hormone insulin, which controls the uptake of glucose by your cells. If you have any excess glucose, this is converted into glycogen – which is stored in the muscles, liver or in fat around the body.
When your body needs more energy, a second hormone called glucagon is secreted by the pancreas. This converts the glycogen back into glucose, which is then released into your bloodstream for your cells to use. This means the body’s glucose (sugar) metabolism is a cycle of glucose, insulin and glucagon reactions.
- The slower the release of glucose and hormones, the more stable and sustainable the energy levels of the body.
- The more refined the carbohydrate, the faster the glucose is released into your blood.
- However during exercise when we burn fuel we need to maintain a constant flow of glucose otherwise we will burn out, in other words “hit the wall”. Although stored fat in our bodies is a second source of fuel during running it cannot be converted to energy unless there is carbohydrate (sugars) present.
Found this great table on the internet!!
When should I consume complex or simple carbohydrates?
During and immediately after runs we need a faster supply of energy to our working muscles and brain, therefore it is recommended that in these times we consume simple carbohydrates.
In all other times we should try and reduce intake of simple sugars and consume only slow releasing low GI wholegrain carbohydrates which will sustain your over all energy levels better.
How much carbohydrate should I take per hour of running?
Research has indicated that Ingested single source carbohydrate is oxidized at 60-70 g.h¯¹. This effectively means that the body cannot digest more that 70g of carbohydrate per hour of exercise and consuming more than this is likely to be associated with gastrointestinal symptoms due to dehydration and slowed gastric emptying.
What happens in my stomach during running?
During exercise the blood flow to the stomach is reduced making it difficult to digest solids and many athletes suffer from cramping and stomach discomfort if they eat meals prior to or snacks during exercise. Sports drinks are designed to quickly pass through the stomach and are rapidly absorbed from the small intestine. They contain just the right amount of carbohydrate that you need along with fluids to prevent dehydration.
What are Sports Drinks?
There are 2 Types of sports drinks available on the market:
Fluid Replacement Drinks – Absorbed faster and contain less electrolytes and sugars.
Energy Drinks – Provide more carbohydrate for energy.
- Hypotonic – 4g CHO /100ml are more effective when rapid rehydration is required and are absorbed faster than water.
- Isotonic – 4-8g CHO/100ml, same osmolality as body fluids, provide ideal rehydration and refuelling; absorbed as fast as plain water.
- Hypertonic – 8g CHO/100ml slower absorption providing more fuel and can dehydrate, most energy drinks are in this category and are not suitable for sport.
In general the isotonic drink is the easiest absorbed and optimally should contain between 6-8% carbohydrate.
What else is in a Sports Drink?
Most sports drinks will also contain electrolytes such as sodium and potassium. These too have their benefits during exercise in that sodium will increase the thirst sensation, aid fluid retention and increase absorption. Potassium assists muscle contractions during exercise. Some drinks contain caffeine and most of them contain artificial preservations, colours and flavours.
Can I make my own Sports Drinks?
Yes of course!!!!!!!!!!
For those of you that prefer to consume healthier and natural products then you can DIY your own sports drink. Coconut water for example is high in antioxidants and electrolytes, why not add organic fruit squash and a pinch of salt to the coconut water for your own homemade drink or try out these two below. I have attached a couple of different drinks recipes that you may like to try…
Homemade Hypotonic Drink
- 250ml Fruit Juice
- 750ml Filtered Water
- ¼ tsp Salt (optional)
- (24g cho per litre)
Homemade Isotonic Drink
- 500ml Fruit Juice
- 500ml Fruit Juice
- ¼ tsp Salt (optional)
- (48g cho per litre)
Final Note
It is really important to remember that we are all individuals and what works for one person may not for another. Never ever try something on race day that you have not recently tried during training runs. Also to note fructose or fruit sugar car irritate the tummy in high amounts and cause diarrhoea. Research indicates that mixing your carbohydrate sources is the best way to take it during exercise, so glucose and fructose together for example. If you have no problem eating solids during running remember to make sure they are high GI and are low in protein and fat. Remember to also try and avoid high fibre foods in this time as otherwise you might end up with a toilet issue! If you take gels you need to drink plenty of water at the same time and avoid taking them with sports drinks as the carbohydrate concentrations will then be too high! High amounts of carbohydrates that are present in concentrated form as is in gels can cause tummy upset, dehydration and cramping when taken without water!!!
Personally I have tried gels and sports drinks recently and found the cyto powder to be pleasant enough and also the homemade isotonic drink is good but I found it to be less effective..is this the placebo effect I wonder?? The gels I find really sticky, sickly and not very palatable and even though I drank a lot of water when taking them I noticed I get stitches about 10-15 minutes after which I found hard to shake off! On the plus side to taking the gels, the days I took them i noticed my recovery following the long run was much quicker than when I just took the sports drinks alone.
Below I have included some tables that will give you the macronutrient values of some common foods. This should help you add up the carbohydrate content of your snacks. Try and plan each hour of long running and start taking your carbohydrate early into the run for example:
- 1st hour: 500ml sports drink
- 2nd hour: Sports Gel with 600ml water
- 3rd hour: Dried Raisins with 500ml water
- 4th hour: Banana, 5-6 natural jellies and 500ml water
Or alternatively do the same thing every hour if that works for you. The biggest problem practically is carrying everything, so for your training runs maybe plan your route in advance and leave drinks along the way, carry a small rucksack or belt to hold the food/gels.
If you have experience with a great drink or you have a magic potion/recipe, then please share with us! It would be really interesting if we could make a product hit list which covers taste, price and results…Alternatively if you have any questions about sports nutrition or hydration then please post on the blog and I’ll do my best to post an answer
Happy running everyone!!
P.S: Please note due to their high sugar content sports drinks are only suitable for consumption around exercise and are not recommended to be taken by children especially outside of sport.
Sports Snack Foods – Macronutrient Values
Fruit
[table]
Food Type,Quantity,Carbohydrate g,Protein g ,Fat g
Banana,1 (100g),23,1.3,0.3
Apple,1 (100g),11.4,0.5,0.1
Pear,1 (100g),10.4,0.3,0.1
Strawberries,100g,6,0.8,0.1
Blueberries,30g,2.1,0.2,0.1
Water Melon,100g,7.1,0.5,0.3
Kiwi,1,6.4,0.7,0.3
Orange,1 (160g),13.6,1.8,0.2
Clementine,1 (60g),5.2,0.5,0.1
Avocado,1 (160g),2.7,2.7,27
Mango,1 (140g),19.7,1,0.3
Dried Raisins,50g,35,1.1,0.2
Dried Apricots,70g,30,3.4,0.5
[/table]
Snacks
[table]
Food Type,Quantity,Carbohydrate g,Protein g ,Fat g
Popcorn Homemade,30g (Popped),23,3.9,1.4
Popcorn Manhatten,1 30g Bag,21,3,4.4
Corn Cakes ÐMultigrain Kelkin,1 cake,10.6,1.8,0.9
Rice Cakes with Yogurt- Kelkin,1 Cake,11.6,1.1,4.1
Bounce Balls-Almond proteinblast,1 Ball 49g,19.4,15,8
Bounce Balls ÐFudgie walnut,1 Ball 42g,20,5,9
Bounce Balls Ð Cashew Pecan,1 Ball 42g,22,4,9
Nature Valley Honey and Oats,1 Bar,32,4,6
Nakd Cocoa orange,1 Bar,16.8,3.9,7
Nakd Cocoa Mint,1 Bar,18.3,3.2,5.4
Nakd Oaty bar banana bread,1 Bar,38,3.2,4.7
Nakd Oaty bar berry Cheeky bar,1 Bar,40,5.3,6.2
Nakd Oary bar Apple Pie,1 Bar,41,75.1,6
[/table]
Vegetables
[table]
Food Type,Quantity,Carbohydrate g,Protein g ,Fat g
Carrots Sticks,80g,4.8,0.6,0.5
Celery,1 stick,0.5,0.3,0.2
Peppers,? in sticks,6.8,1,0.3
Tomato,1,2.6,0.6,0.3
Cherry Tomato,5,3,0.8,0.4
[/table]
Breads
[table]
Food Type,Quantity,Carbohydrate g,Protein g ,Fat g
Wholemeal bagel,1 (82g),43,9.8,1.8
Wholemeal Pita,1 (67g),39,6.2,0.8
Brown bread,1 slice (80g),26,4.7,0.8
Soft Bread rolls,1 roll (56g),28,5.1,1.4
[/table]
Toppings for Bread
[table]
Food Type,Quantity,Carbohydrate g,Protein g ,Fat g
Honey,1 tsp,7.6,0,0
Jam,1 tsp,2.4,0.1,0
Butter,1 tsp,0,0,4.1
Nutella,20g,12.1,1.2,6.6
Almond Butter,1 tbsp,1.2,3.8,10
Peanut Butter,1 tbsp,1.4,4.5,9.6
Ham,1 slice,0.1,4.2,1
Cheddar ,1 slice 22g,0,5.5,7.4
[/table]
Recipes
Click below for some recipes for home made sports drinks